







InstElectric - Electricity

คำอธิบายของInstElectric - Electricity
Tool to support the calculation of electrical installations that will allow the user (designer / electrician / technician) to perform electrical calculations easily and quickly.
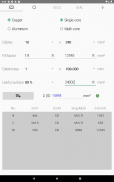
· Dimensioning complete of low voltage circuits with the most frequent installation methods
· Phase cable size, neutral, protective conductor
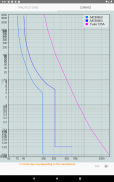
· Criteria based on the admissible current of the cable, voltage drop and overcurrent protection
· Designation of the most used cables.
· Circuits with automatic circuit breaker until In = 4000 A (Ir rating setting), maximum fuse In = 1600 A (gG type), maximum 12 conductors parallel per phase, maximum size 630 mm²
· Estimate of the maximum short-circuit current (simplified method)
· Forecast of loads of a building destined to houses with several sections: dwellings, common services, commercial premises/offices and garage with/without infrastructure for recharging electric vehicles
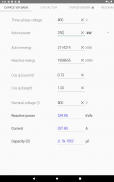
· Reactive power of the capacitor bank for the compensation of the power factor (cos φ) and capacity (µF) of the capacitors
· C/K Factor for automatic capacitor bank
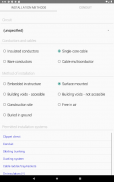
· Choice of installation system in the function of the circuit, cable and its situation
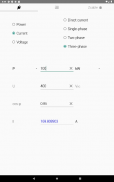
· Power in an unbalanced three-phase system
· Overvoltages due to loss of neutral conductor, earth fault and short circuit
· Electricity parameters of a single-phase or three-phase (balanced)
· Transformer performance
· Secondary voltage of a transformer acoording to switch position
· Size of trays and conduits
· Conduits characteristics according to the installation method
· Conversions of wire sizes (mm²-awg) and conduits threads
Parameter settings for calculations:
· Constants (voltages, conductivity, temperatures, etc.) that affect electrical calculations
· Protections (circuit breakers and fuses)
· Selection of minimum rate for circuit-breakers with regulation and maximum cable size for multi-conductor grouping per phase
· Method estimation of the reactance
· Conductivity of the conductor depending on the current of the circuit (constant, according to the expected current, maximum cable temperature)
· Use reduction factors by grouping cables/circuits
· Use of factors of diversity/utilization
· Reference documents: IEC Standards, REBT (sp), Technical Application Guide, (UE) 2016/364
IN NO CASE SHALL THE AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT OR INDIRECT DAMAGES AS A RESULT OF THE CORRECT OR INCORRECT USE OF THE APPLICATION
เครื่องมือที่สนับสนุนการคำนวณการติดตั้งระบบไฟฟ้าที่จะช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ (นักออกแบบ / ช่างไฟฟ้า / ช่างเทคนิค) ทำการคำนวณทางไฟฟ้าได้ง่ายและรวดเร็ว
·การวัดขนาดของวงจรแรงดันไฟฟ้าต่ำด้วยวิธีการติดตั้งที่บ่อยที่สุด
·ขนาดสายเฟส, เป็นกลาง, ตัวนำป้องกัน
·เกณฑ์ขึ้นอยู่กับกระแสที่ยอมรับได้ของสายเคเบิล, แรงดันไฟฟ้าตกและการป้องกันกระแสไฟฟ้าเกิน
·การกำหนดสายเคเบิลที่ใช้มากที่สุด
·วงจรที่มีเบรกเกอร์อัตโนมัติจนถึงใน = 4000 A (การตั้งค่าคะแนน Ir), ฟิวส์สูงสุดใน = 1600 A (ประเภท gG), ตัวนำสูงสุด 12 ขนานต่อเฟส, ขนาดสูงสุด 630 มม. ²
·ประมาณการกระแสไฟฟ้าลัดวงจรสูงสุด (วิธีที่ง่าย)
·การคาดการณ์การโหลดของอาคารที่กำหนดไว้สำหรับบ้านที่มีหลายส่วน: อาคารบ้านเรือนบริการทั่วไปสถานที่เชิงพาณิชย์ / สำนักงานและโรงจอดรถที่มี / ไม่มีโครงสร้างพื้นฐานสำหรับการชาร์จรถยนต์ไฟฟ้า
·พลังงานปฏิกิริยาของธนาคารตัวเก็บประจุเพื่อชดเชยค่าตัวประกอบกำลัง (cos φ) และความจุ (µF) ของตัวเก็บประจุ
· C / K Factor สำหรับธนาคารตัวเก็บประจุอัตโนมัติ
·ทางเลือกของระบบการติดตั้งในการทำงานของวงจรสายเคเบิลและสถานการณ์
·กำลังไฟในระบบสามเฟสที่ไม่สมดุล
·แรงดันไฟฟ้าเกินเนื่องจากการสูญเสียของตัวนำเป็นกลางความผิดดินและไฟฟ้าลัดวงจร
·ค่าไฟฟ้าของเฟสเดียวหรือสามเฟส (สมดุล)
·ประสิทธิภาพของหม้อแปลง
·แรงดันทุติยภูมิของหม้อแปลง a ตามการสลับตำแหน่ง
·ขนาดของถาดและท่อร้อยสายไฟ
·ลักษณะเฉพาะของท่อร้อยสายตามวิธีการติดตั้ง
·การแปลงขนาดสายไฟ (mm²-awg) และชุดสายไฟ
การตั้งค่าพารามิเตอร์สำหรับการคำนวณ:
·ค่าคงที่ (แรงดันไฟฟ้า, การนำไฟฟ้า, อุณหภูมิ, ฯลฯ ) ที่มีผลต่อการคำนวณทางไฟฟ้า
·การป้องกัน (เบรกเกอร์วงจรและฟิวส์)
·การเลือกอัตราขั้นต่ำสำหรับเบรกเกอร์วงจรที่มีการควบคุมและขนาดสายเคเบิลสูงสุดสำหรับการจัดกลุ่มหลายตัวนำต่อเฟส
·การประมาณค่าวิธีปฏิกิริยารีแอกแตนซ์
·ค่าการนำไฟฟ้าของตัวนำขึ้นอยู่กับกระแสของวงจร (ค่าคงที่ตามกระแสที่คาดไว้อุณหภูมิของสายเคเบิลสูงสุด)
·ใช้ปัจจัยการลดลงโดยการจัดกลุ่มสายเคเบิล / วงจร
·การใช้ปัจจัยด้านความหลากหลาย / การใช้ประโยชน์
·เอกสารอ้างอิง: มาตรฐาน IEC, REBT (sp), คู่มือการใช้งานด้านเทคนิค, (UE) 2016/364
ไม่ว่าในกรณีใดผู้ใช้จะต้องรับผิดชอบต่อความเสียหายโดยตรงหรือความเสียหายใด ๆ ที่เป็นผลของการใช้งานที่ถูกต้องหรือไม่ถูกต้องของแอปพลิเคชัน
























